Semi-Rigid Coax Selector Guide
Standard Coax Diameters from .031 to .250 inches
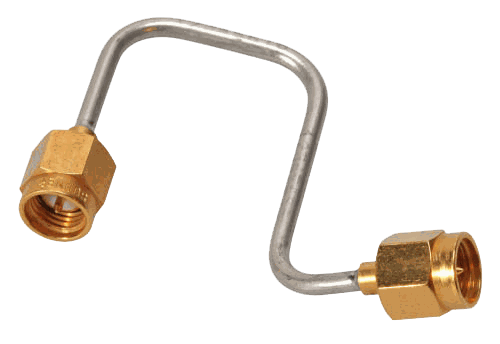
We use our Semi-Rigid Coax to build Cable Assemblies
Choose to build your own semi-rigid cables or we can do it for you
Semi-Rigid Features
A variety of Impedance and Construction Options
P1dB semi-rigid coax is used to build semi-rigid assemblies for test equipment, aerospace, wireless, medical and low PIM applications. The advantage of semi-rigid coax over flexible coax is its increased phase stability and lower insertion loss. Semi-rigid coax also provides the best electrical isolation and lower noise levels when compared to flexible coax.
Another advantage of semi-rigid coax is that it can be bent into and hold intricate shapes to accommodate complex cable runs, such as inside a chassis. Semi-rigid is very durable and can survive harsh shock and vibration environments, such as a jet fighter or a missile. It can also handle large temperature swings, depending on the coax dielectric.
P1db Semi-rigid is available in 10 Ohm, 17 Ohm, 25 Ohm, 50 Ohm, 75 Ohm and 93 Ohm impedances with solid PTFE, low-density PTFE (LD PTFE) or FEP dielectric. The diameters available are .031 inch, .034 inch, .047 inch, .070 inch, .085 inch, .118 inch, .130 inch, .141 inch and .250 inch with a bare copper, tinned copper, silver plated copper, tinned aluminum or stainless steel outer conductor. Two types of center conductors are offered, which are silver plated copper (SPC) easier bending or silver plated copper clad steel (SPCW) for high vibration applications. All raw semi-rigid coax types are sold in straight sections, depending on the coax diameter. Check the individual semi-rigid coax page for its specific straight-section length.
Semi-Rigid Features
- Impedance values from 10 to 93 Ohms
- Diameters from .031 inches to .250 inches
- Standard (PTFE and FEP) and low loss (LD PTFE) version
- Outer Conductor options from Bare Copper, Tinned Copper, Tinned Aluminum and more
- Semi-Rigid Coax is sold in 1 to 2-meter lengths, depending on the coax diameter
Phase-matched cables are offered in both flexible and semi-rigid coax, but semi-rigid offers the best performance and stability. This is because semi-rigid coax will not flex, therefore phase-over-flexure errors on non-existent. Their ability to hold a shape, phase stability and their high power capability are reasons why these cables are also preferred for coaxial baluns and transformers in applications, such as in a high power RF amplifier or pallet.
P1dB has a large selection of semi-rigid coax at a very competitive price. The types of coax are shown below in 3 categories, .085 and .141 50 Ohm Coax, More 50 Ohm Coax Diameters, and Other Impedance Coax. Our semi-rigid is broken into 3 groups below for your convenience. They are .085 and .141 50 Ohm coax, other 50 Ohm diameter coax, and
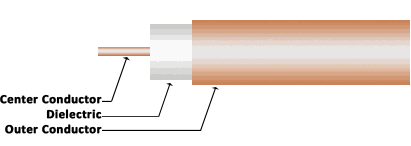
.085 and .141, 50 Ohm Coax - The most common diameters for semi-rigid cable assemblies, due to a wide selection of connectors. A bare copper outer conductor is the most common type, but many customers prefer tinned copper for its solder-ability when assembling their own cables. For situations where increased conductivity is needed, then Silver plated copper is the best choice. Metals other than copper are also available, such as Tinned Aluminum for weight concerns and Stainless Steel for harsh environments. There are two choices for a dielectric, PTFE for common applications and LD PTFE for low loss requirements.
| Part Number | Impedance (Ω) | Diameter (in.) | Outer Conductor | Center Conductor | Dielectric |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1CB-050-085-CUSP-L | 50 | .085 | Bare Copper | SPC | LD PTFE |
| P1CB-050-085-CUSW-P | 50 | .085 | Bare Copper | SPCW | PTFE |
| P1CB-050-085-SPSP-L | 50 | .085 | Silver Plated Copper | SPC | LD PTFE |
| P1CB-050-085-SPSW-P | 50 | .085 | Silver Plated Copper | SPCW | PTFE |
| P1CB-050-085-SSSW-P | 50 | .085 | Stainless Steel | SPCW | PTFE |
| P1CB-050-085-TASP-L | 50 | .085 | Tin Plated Aluminum | SPC | LD PTFE |
| P1CB-050-085-TASW-P | 50 | .085 | Tin Plated Aluminum | SPCW | PTFE |
| P1CB-050-085-TPSP-L | 50 | .085 | Tin Plated Copper | SPC | LD PTFE |
| P1CB-050-085-TPSW-P | 50 | .085 | Tin Plated Copper | SPCW | PTFE |
| P1CB-050-141-CUSP-L | 50 | .141 | Bare Copper | SPC | LD PTFE |
| P1CB-050-141-CUSW-P | 50 | .141 | Bare Copper | SPCW | PTFE |
| P1CB-050-141-SPSP-L | 50 | .141 | Silver Plated Copper | SPC | LD PTFE |
| P1CB-050-141-SPSW-P | 50 | .141 | Silver Plated Copper | SPCW | PTFE |
| P1CB-050-141-SSSW-P | 50 | .141 | Stainless Steel | SPCW | PTFE |
| P1CB-050-141-TASP-L | 50 | .141 | Tin Plated Aluminum | SPC | LD PTFE |
| P1CB-050-141-TASW-P | 50 | .141 | Tin Plated Aluminum | SPCW | PTFE |
| P1CB-050-141-TPSP-L | 50 | .141 | Tin Plated Copper | SPC | LD PTFE |
| P1CB-050-141-TPSW-P | 50 | .141 | Tin Plated Copper | SPCW | PTFE |
More 50 Ohm Coax Diameters
– Higher frequency applications, such as 60 GHz, require smaller diameter coax cables with higher cutoff frequencies.
For example, a .047 diameter cable has a maximum frequency of 109 GHz, while a .250 diameter coax has a max frequency of 19 GHz.
The
| Part Number | Impedance (Ω) | Diameter (in.) | Outer Conductor | Center Conductor | Dielectric |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1CB-050-031-CUSP-L | 50 | .031 | Bare Copper | SPC | LD PTFE |
| P1CB-050-031-TPSP-L | 50 | .031 | Tin Plated Copper | SPC | LD PTFE |
| P1CB-050-034-CUSW-P | 50 | .034 | Bare Copper | SPCW | PTFE |
| P1CB-050-034-SPSW-P | 50 | .034 | Silver Plated Copper | SPCW | PTFE |
| P1CB-050-034-TPSW-P | 50 | .034 | Tin Plated Copper | SPCW | PTFE |
| P1CB-050-047-CUSW-P | 50 | .047 | Bare Copper | SPCW | PTFE |
| P1CB-050-047-SPSW-P | 50 | .047 | Silver Plated Copper | SPCW | PTFE |
| P1CB-050-047-SSSW-P | 50 | .047 | Stainless Steel | SPCW | PTFE |
| P1CB-050-047-TASP-L | 50 | .047 | Tin Plated Aluminum | SPC | LD PTFE |
| P1CB-050-047-TASW-P | 50 | .047 | Tin Plated Aluminum | SPCW | PTFE |
| P1CB-050-047-TPSW-P | 50 | .047 | Tin Plated Copper | SPCW | PTFE |
| P1CB-050-070-CUSP-P | 50 | .070 | Bare Copper | SPC | PTFE |
| P1CB-050-070-SPSP-P | 50 | .070 | Silver Plated Copper | SPC | PTFE |
| P1CB-050-118-CUSW-L | 50 | .118 | Bare Copper | SPCW | LD PTFE |
| P1CB-050-118-SPSW-L | 50 | .118 | Silver Plated Copper | SPCW | LD PTFE |
| P1CB-050-118-TPSW-L | 50 | .118 | Tin Plated Copper | SPCW | LD PTFE |
| P1CB-050-250-CUSP-P | 50 | .250 | Bare Copper | SPC | PTFE |
| P1CB-050-250-SPSP-P | 50 | .250 | Silver Plated Copper | SPC | PTFE |
| P1CB-050-250-TASP-P | 50 | .250 | Tin Plated Aluminum | SPC | PTFE |
| P1CB-050-250-TPSP-P | 50 | .250 | Tin Plated Copper | SPC | PTFE |
Other Impedance Coax –
| Part Number | Impedance (Ω) | Diameter (in.) | Outer Conductor | Center Conductor | Dielectric |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1CB-010-034-CUSP-F | 10 | .034 | Bare Copper | SPC | FEP |
| P1CB-010-043-SPSP-F | 10 | .043 | Silver Plated Copper | SPC | FEP |
| P1CB-010-070-CUSP-F | 10 | .070 | Bare Copper | SPC | FEP |
| P1CB-010-070-SPSP-F | 10 | .070 | Silver Plated Copper | SPC | FEP |
| P1CB-017-034-CUSP-P | 17 | .034 | Bare Copper | SPC | PTFE |
| P1CB-025-034-CUSW-P | 25 | .034 | Bare Copper | SPCW | PTFE |
| P1CB-025-070-CUSP-F | 25 | .070 | Bare Copper | SPC | FEP |
| P1CB-025-070-SPSP-F | 25 | .070 | Silver Plated Copper | SPC | FEP |
| P1CB-025-070-TPSP-F | 25 | .070 | Tin Plated Copper | SPC | FEP |
| P1CB-025-090-CUSP-P | 25 | .090 | Bare Copper | SPC | PTFE |
| P1CB-025-125-CUSP-P | 25 | .125 | Bare Copper | SPC | PTFE |
| P1CB-075-085-CUSW-P | 75 | .085 | Bare Copper | SPCW | PTFE |
| P1CB-075-090-CUSP-F | 75 | .090 | Bare Copper | SPC | FEP |
| P1CB-075-141-CUSW-P | 75 | .141 | Bare Copper | SPCW | PTFE |
| P1CB-093-130-CUSW-P | 93 | .130 | Bare Copper | SPCW | PTFE |


